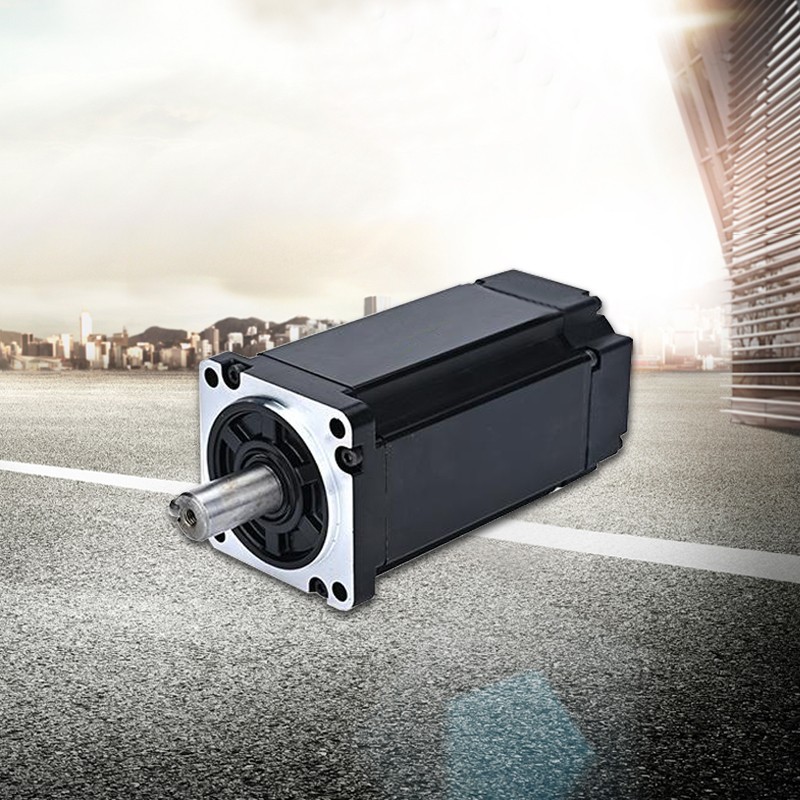
What are the components of a brushless motor?
A brushless motor is composed of a motor body, an electronic speed controller, and sensors. The main body of an electric motor is the core part of the motor, usually composed of a rotor and a stator.
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, supported by permanent magnets and bearings. The stator is a fixed part of the motor, usually composed of coils and iron cores. Electronic speed controller is a key device for controlling the speed and output power of brushless motors. It receives feedback signals from sensors and processes them to provide appropriate current and voltage to the motor. Sensors are used to detect parameters such as motor speed, position, and temperature, and transmit this information to electronic speed controllers for accurate control and regulation.
The working principle of brushless motors is based on electromagnetic induction and electronic speed regulation technology. When current passes through the stator coil, a magnetic field is generated, which interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, causing the rotor to rotate under the action of torque. The electronic speed controller controls the magnitude and direction of the current based on the feedback signal from the sensor, thereby controlling the speed and output power of the motor. Brushless motors have the advantages of simple structure, small size, high power density, high efficiency, low noise, and long lifespan, and are widely used in industries, transportation vehicles, household appliances, and robots.
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor, supported by permanent magnets and bearings. The stator is a fixed part of the motor, usually composed of coils and iron cores. Electronic speed controller is a key device for controlling the speed and output power of brushless motors. It receives feedback signals from sensors and processes them to provide appropriate current and voltage to the motor. Sensors are used to detect parameters such as motor speed, position, and temperature, and transmit this information to electronic speed controllers for accurate control and regulation.
The working principle of brushless motors is based on electromagnetic induction and electronic speed regulation technology. When current passes through the stator coil, a magnetic field is generated, which interacts with the permanent magnets on the rotor, causing the rotor to rotate under the action of torque. The electronic speed controller controls the magnitude and direction of the current based on the feedback signal from the sensor, thereby controlling the speed and output power of the motor. Brushless motors have the advantages of simple structure, small size, high power density, high efficiency, low noise, and long lifespan, and are widely used in industries, transportation vehicles, household appliances, and robots.